Magnesium and graphite: an electricity experiment #science #chemistry #cathode #anode #physics
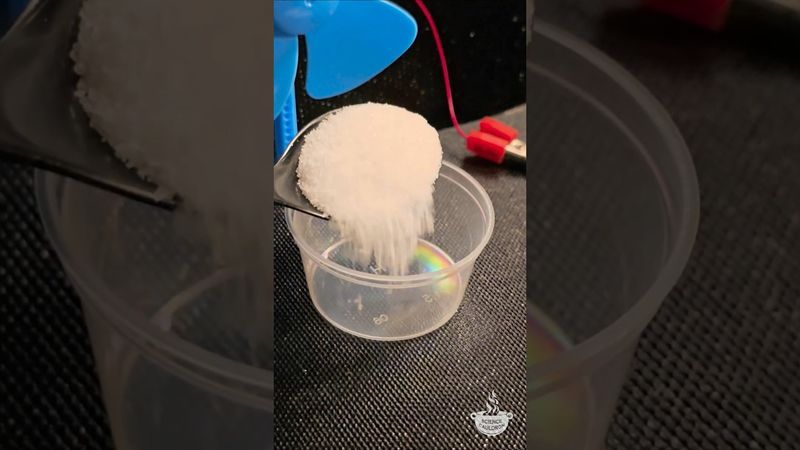

معلومات تحميل وتفاصيل الفيديو Magnesium and graphite: an electricity experiment #science #chemistry #cathode #anode #physics
المؤلف:
Science Cauldronتاريخ النشر:
17/12/2025المشاهدات:
2.1Kالوصف:
فيديوهات مشابهة: Magnesium and graphite

Урок №37. Необратимый гидролиз бинарных соединений и солей и некоторые ОВР

Reactivity of Alkali Metals with Water
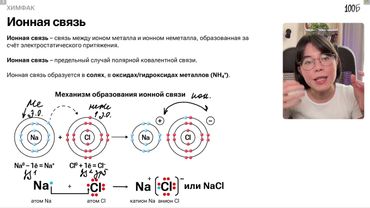
Урок №07 Ионная связь Металлическая связь Водородная связь

Урок №88. Водород. Кислород. Пероксид водорода

Урок №76. Алюминий, бериллий, цинк и их соединения

