Magnesium and graphite: an electricity experiment #science #chemistry #cathode #anode #physics
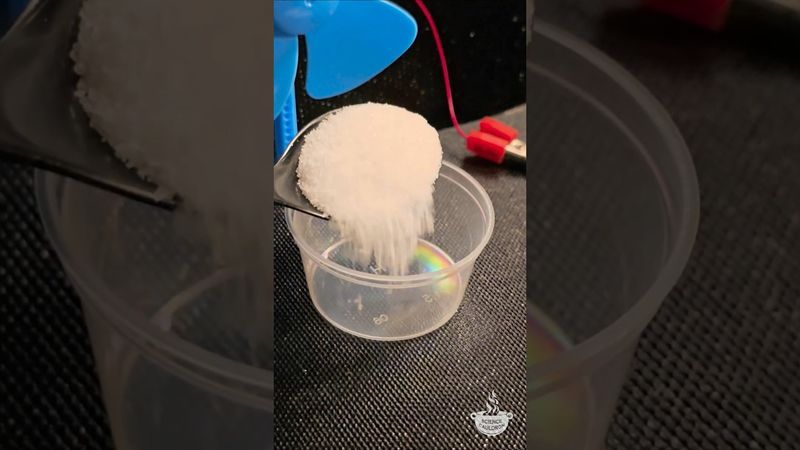

Magnesium and graphite: an electricity experiment #science #chemistry #cathode #anode #physics 影片的下載資訊和詳情
作者:
Science Cauldron發布日期:
2025/12/17觀看次數:
2.1K簡介:
相似影片:Magnesium and graphite

Урок №37. Необратимый гидролиз бинарных соединений и солей и некоторые ОВР

Reactivity of Alkali Metals with Water
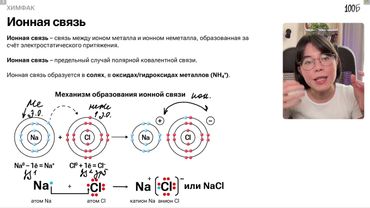
Урок №07 Ионная связь Металлическая связь Водородная связь

Урок №88. Водород. Кислород. Пероксид водорода

Урок №76. Алюминий, бериллий, цинк и их соединения

